What is a Crypto Wallet?
Crypto wallet is a digital tool that allow users to store, manage, and interact with their cryptocurrencies. Essentially, a crypto wallet don’t store the actual coins but rather the keys used to access and authorize transactions on the blockchain.
Each Crypto wallet hold pairs of cryptographic keys: a public key (address) that others use to send cryptocurrency to you and a private key that you use to access and manage your holdings.
Some Cryptocurrency exchanges offers their own Wallets such as Coinbase to store your Cryptocurrencies.
Importance of Crypto Wallet
Crypto Wallets play a crucial role in the cryptocurrency ecosystem by providing a secure means for users to store and transact with their digital assets. Crypto wallets act as a bridge between the user and the blockchain, enabling the sending and receiving of cryptocurrencies while ensuring the security of the associated keys. Without wallets, users would not have a practical way to manage their crypto holdings or engage in transactions.
Types of Crypto Wallets
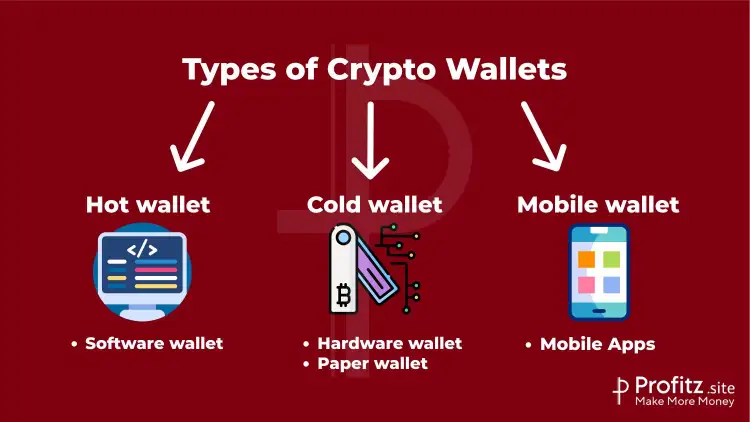
1. Hot Wallets
Hot wallets are connected to the internet and are more convenient for frequent transactions. They are easily accessible through various devices and platforms, making them suitable for active trading or spending. However, they are more susceptible to hacking or unauthorized access due to their online connectivity.
2. Cold Wallets
Cold wallets, on the other hand, are offline storage solutions, keeping the private keys completely disconnected from the internet. This makes them highly secure against online threats like hacking or malware. Hardware and paper wallets are examples of cold wallets.
3. Hardware Wallets
Hardware wallets are physical devices specifically designed for securely storing cryptocurrency keys. They are considered one of the safest options as they store the keys offline and often require physical interaction to authorize transactions, adding an extra layer of security.
Hardware wallets are dominated by Trezor, Ledger, Billfodl by Privacypros

4. Paper Wallets
Paper wallets involve printing out the public and private keys on a physical piece of paper, which is then kept securely. While they provide a high level of security by keeping keys offline, they require careful handling to prevent loss or damage.


5. Mobile Wallets
Mobile wallets are smartphone applications that enable users to manage their cryptocurrencies on the go. They offer convenience but may not provide the same level of security as hardware or paper wallets due to the potential vulnerabilities of mobile devices.
Recommended Mobile wallets are Trust Wallet, Exodus has both web application & Mobile app.
You can see the reviews of Best Wallets here.
How Crypto Wallet Store Private and Public Keys
Crypto wallet serve as digital containers for storing private keys, essential components for accessing and controlling one’s cryptocurrency holdings. Understanding how Crypto wallet handle these keys is fundamental to comprehending their security and functionality.

1. Private Keys
These are akin to passwords or secret codes granting access to your cryptocurrency. They are mathematically linked to public keys and wallet addresses. Private keys must remain confidential and secure at all costs.
2. Public Keys
Generated from private keys through complex mathematical algorithms, public keys are openly shared and serve as addresses where others can send cryptocurrencies. They’re derived from the private key but cannot reverse-engineer the private key.
3. Address Generation
Wallets use cryptographic algorithms to generate pairs of public and private keys. These keys are usually represented as long strings of alphanumeric characters. For every public key, there’s a corresponding private key.
4. Storage Methods
Wallets employ various storage methods for keys, depending on their type.
Hot Wallets: Typically store keys online, making them more vulnerable to hacking.
Cold Wallets: Store keys offline, adding a layer of security but potentially making transactions slower.
5. Cryptography and Security Measures
Wallets use advanced cryptographic techniques to secure private keys within their systems. Encryption, hashing, and other cryptographic protocols safeguard keys from unauthorized access.
6. Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) Wallets
3Some modern wallets use HD technology, enabling the generation of multiple key pairs from a single seed phrase. This enhances security and ease of backup.
How Crypto Wallet Works
Cryptocurrency wallets are the gateways that enable users to interact with blockchain networks by managing their digital assets. Understanding how these wallets function provides insight into their security, usability, and the mechanisms behind sending and receiving cryptocurrencies.
A. Address Generation and Encryption
- Address Generation: Each cryptocurrency wallet generates unique addresses associated with a user’s account. These addresses are alphanumeric strings that serve as destinations for sending or receiving funds.
- Public and Private Keys: Wallets use cryptographic keys—public and private—to facilitate transactions. The public key functions as the wallet address visible to others, while the private key, kept securely within the wallet, is used to authorize outgoing transactions. The encryption ensures secure communication and ownership verification.
B. Sending and Receiving Cryptocurrencies
- Transaction Initiation: When sending cryptocurrency, the sender initiates a transaction by specifying the recipient’s wallet address and the amount to be sent. The transaction is then broadcast to the network.
- Confirmation Process: Transactions are grouped into blocks and added to the blockchain through a consensus mechanism (e.g., Proof of Work or Proof of Stake). Miners or validators confirm these transactions, ensuring their validity and adding them to the immutable ledger.
- Wallet Synchronization: Wallets sync with the blockchain to reflect the most current transaction history and account balances. This synchronization varies based on the type of wallet (e.g., full node wallets sync the entire blockchain).
C. Wallet Security Features and Mechanisms
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adding an extra layer of security, 2FA requires users to verify their identity using a secondary method (e.g., SMS code, authenticator app) in addition to their password when accessing the wallet.
- Multi-Signature Wallets: These wallets require multiple private keys to authorize transactions, enhancing security by necessitating the approval of multiple parties. For instance, a wallet may require two out of three private keys to complete a transaction.
- Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) Wallets: HD wallets generate a sequence of public and private keys from a single seed. This feature streamlines the backup process, generates multiple addresses, and enhances privacy by using a new address for each transaction.
Choosing the Right Crypto Wallet
Selecting the perfect cryptocurrency wallet is pivotal in safeguarding your digital assets. Consider the following factors before making your decision:
1. Security
The paramount concern when choosing a wallet is its security features. Look for wallets with robust encryption, two-factor authentication (2FA), and a strong reputation for safeguarding against cyber threats. Hardware wallets, known for their offline storage and limited exposure to online risks, often rank high in terms of security.
2. User-friendliness
Ease of use plays a significant role, especially for newcomers to the crypto space. Opt for wallets with intuitive interfaces and straightforward navigation. Wallets like MetaMask and Trust Wallet offer simplicity without compromising on security, making them ideal for beginners and experienced users alike.
3. Supported Cryptocurrencies
Ensure the wallet supports the cryptocurrencies you intend to store or transact with. Some wallets are tailored for specific coins or have limitations on the number of cryptocurrencies they can accommodate. For diversified portfolios, wallets like Exodus, which support a wide array of tokens, might be preferable.
4. Mobility
Consider your lifestyle and the need for access on the go. Mobile wallets, available as smartphone apps, offer convenience and accessibility, allowing you to manage your funds wherever you are. Wallets like Coinomi or MyEtherWallet (MEW) provide this flexibility without compromising security.
5. Cost
While many Crypto wallets are free to download and use, some might have associated costs. Hardware wallets often come with an initial purchase price, but they provide unparalleled security. Additionally, watch out for transaction fees associated with certain wallets, which can impact your overall costs, especially if you’re a frequent trader.
Here’s a blog on Crypto wallets with Lowest Transaction fees.
By weighing these factors against your specific needs and preferences, you can make an informed choice when selecting a crypto wallet that aligns best with your requirements.
Comparison of the best wallets
Choosing the right cryptocurrency wallet is crucial for the security and convenience of managing your digital assets. Here’s a comparative analysis of some popular wallets:
1. Exodus
Exodus is a user-friendly desktop and mobile wallet known for its intuitive interface and support for a wide range of cryptocurrencies. It provides a built-in exchange feature, allowing users to swap assets without leaving the wallet. While it offers convenience, it’s a hot wallet, meaning it’s connected to the internet, potentially making it more vulnerable to cyber threats.
2. Ledger Nano S/X
Ledger Nano S and Ledger Nano X are hardware wallets, offering top-notch security by keeping private keys offline. They support a multitude of cryptocurrencies and are especially ideal for long-term storage due to their enhanced protection against online hacking attempts. However, they might not be as convenient for frequent transactions as mobile wallets.
3. Trezor
Similar to Ledger, Trezor is a hardware wallet that emphasizes security. It’s renowned for its open-source approach and transparency in design. Trezor devices support various cryptocurrencies and integrate with third-party applications. The user interface might be less intuitive for beginners compared to other wallets.
4. MetaMask
MetaMask is a popular browser extension wallet primarily used for interacting with decentralized applications (dApps) on the Ethereum blockchain. It provides a convenient gateway to the world of DeFi and allows users to manage Ethereum-based tokens. However, it’s a hot wallet and relies on the security of the connected browser.
5. Trust Wallet
Trust Wallet is a mobile wallet offering a seamless and user-friendly experience, especially for those diving into the world of decentralized finance. It supports a wide array of cryptocurrencies and tokens, and its integration with decentralized exchanges adds to its appeal. Being a mobile wallet, it offers convenience but requires careful device security measures.
When choosing a wallet, consider factors such as security features, ease of use, supported cryptocurrencies, your intended usage (long-term storage or frequent transactions), and your comfort level with the technology involved. Always prioritize security and choose a wallet that aligns with your specific needs and preferences.
| Wallet Name | Type | Supported Cryptocurrencies | Security Features | User-Friendliness | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exodus | Desktop/Mobile | 100+ | Two-factor authentication, Backup passphrase | Intuitive interface, Suitable for beginners | Free (with transaction fees) |
| Ledger Nano S/X | Hardware | 1,500+ | Secure chip technology, PIN code, Recovery phrase | Advanced security, Requires technical setup | Paid (one-time purchase) |
| Trezor | Hardware | 8,000+ | PIN protection, Recovery seed, Passphrase support | User-friendly, Secure storage | Paid (one-time purchase) |
| MetaMask | Browser/Extension | Ethereum & ERC-20 tokens | Seed phrase, Integration with dApps | Easy setup, Ideal for Ethereum users | Free |
| Trust Wallet | Mobile | 30,000+ | Secure storage, Passcode, Multi-currency support | Beginner-friendly, Mobile convenience | Free |
Setting Up and Using a Cryptocurrency Wallet
1. Creating a New Wallet
Creating a cryptocurrency wallet typically involves these steps:
- Choose Your Wallet Type: Decide between hardware, software, or mobile wallets based on your preferences for security and accessibility.
- Select a Wallet Provider: Opt for a reputable provider or software application. Popular choices include Ledger, Trezor, MetaMask, and Trust Wallet.
- Install the Wallet Application: Download and install the wallet app or access it via a web interface. Follow the instructions to set up your account.
- Generate Your Wallet: Generate your wallet address and private key. Ensure you securely store these details, as they grant access to your funds.
2. Backing Up and Securing Your Wallet
- Create a Backup: Most wallets provide a recovery phrase or seed words. Write this down and store it in a safe place offline. This phrase can be used to recover your wallet if it’s lost or compromised.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enhance security by enabling 2FA wherever possible. This adds an extra layer of protection to your account.
3. Making Transactions
- Receiving Funds: To receive cryptocurrencies, share your wallet address with the sender. Ensure the sender uses the correct address specific to the cryptocurrency you want to receive.
- Sending Funds: Initiate a transaction by entering the recipient’s wallet address and the amount you want to send. Verify the details before confirming the transaction.
4. Checking Balances and History
- Balance Inquiry: Access your wallet dashboard to check your current balances for different cryptocurrencies held in your wallet.
b.Transaction History: Explore the transaction history to review past transactions, including details like transaction IDs, dates, amounts, and status.
By following these steps and maintaining vigilance over your wallet’s security, you can confidently manage your cryptocurrency holdings while minimizing the risks of unauthorized access or loss. Always remember to keep your private keys and recovery phrases safe and secure.
Tips for Safe Wallet Usage
- Backup Your Wallet: Always create backups of your wallet’s private keys or seed phrases. Store these backups securely offline, preferably in multiple locations, to prevent the risk of losing access to your funds due to hardware failure or loss.
- Use Strong Passwords: Strengthen the security of your wallet with a robust, unique password. Avoid using easily guessable phrases or personal information. Consider employing a password manager to generate and store complex passwords securely.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Implementing 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, typically through a mobile app or SMS, for accessing your wallet. This significantly reduces the chances of unauthorized access.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep your wallet software up to date. Developers often release updates that patch security vulnerabilities or introduce new security features. Staying current with updates is crucial for protecting your funds.
- Beware of Phishing and Scams: Be cautious of unsolicited emails, messages, or websites asking for your wallet information or private keys. Always verify the legitimacy of sources before providing any sensitive information. Official wallet providers never ask for private keys directly.
- Verify Addresses Before Transactions: Before sending funds, double-check the recipient’s wallet address. A single character error can result in irreversible loss of funds. Consider copying and pasting addresses rather than typing them out manually.
- Limit Exposure of Private Keys: Avoid sharing your private keys or seed phrases with anyone. Keep them strictly confidential and only accessible to yourself. No legitimate service or support team will ask for this information.
- Use Hardware Wallets for Large Holdings: For significant amounts of cryptocurrency, consider using hardware wallets. These physical devices store keys offline, providing an added layer of security against online threats.
- Test Small Transactions: When using a new wallet or service for the first time, initiate a small transaction to ensure everything works as intended before transferring larger amounts.
- Regularly Monitor Account Activity: Stay vigilant by regularly checking your wallet’s transaction history and account activity. Promptly address any unfamiliar or suspicious transactions.
Recap of Key Points
- Cryptocurrency wallets play a pivotal role in the world of digital assets, serving as the bridge between users and their holdings.
- They come in various forms, from hot wallets for convenient access to cold wallets for enhanced security.
- Private and public key management is crucial for your wallet security. Safeguarding these keys ensures control and ownership of your cryptocurrencies.
- Employ various security features like two-factor authentication, multi-signature capabilities, and hierarchical deterministic structures to fortify their defenses against potential threats.
- Check receipient’s address twice or thrice before sending funds.Always send a small or test fund before bulk transaction.
- Do not disclose your private keys to anyone.Store it offline in 2 or 3 places in hardware wallets.
- Do share your public keys only to legitimate persons after checking their backgrounds.
Conclusion
Before concluding, I want share you something. There are smart ways, sometimes FREE ways to earn Cryptocurrencies. Such ways are Crypto Airdrops (Free Crypto coins), Crypto Bounties (Do a task, Get Cryptocurrency), Crypto faucets, Crypto staking, Yield Farming. You can participate in Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) to get Free Crypto coins. Sometimes without trading, just by exchanging cryptocurrencies you can money too – it’s called Crypto Arbitrage.
Or else you create your own cryptocurrency!!! yes you can through Crypto Mining. Do you know you can start your crypto mining journey in your smartphone ?
Transaction fees is one of the crucial factor to consider for Crypto wallets. Here’s a comparison of Top Crypto Wallets with Lowest Transaction Fees.
Final Thoughts
It’s not just about storing your digital assets but safeguarding them against ever-evolving cyber threats. A well-chosen wallet aligns with your priorities—whether it’s security, convenience, or a balance between the two.
Remember, security practices and precautions are non-negotiable. Regular backups, strong passwords, and staying vigilant against phishing attempts are vital. Striking a balance between security and usability is key to a positive crypto experience.
As the cryptocurrency landscape continues to evolve, so will wallets. Embracing emerging technologies and staying informed about new features and integrations will empower you to adapt and make informed choices in securing and utilizing their crypto assets.
I have summarized some of the commonly used smartest ways to earn Crypto coins.
Happy Trading Crypto !!!
