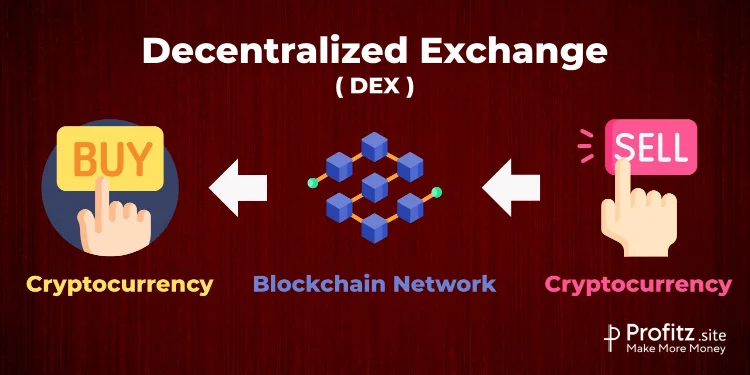
What is a Decentralized Exchange (DEX)?
Decentralized Exchange (DEX) are platforms that enable peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trading without the need for a central authority or intermediary as in Centralized exchanges (CEX). Decentralized Exchange (DEX) operate using smart contracts deployed on blockchain networks, allowing users to trade directly with each other in a decentralized manner.
These smart contracts are automated & executed when certain conditions are met. Transparency in DEX offers the Security in Crypto transactions. Decentralized Exchange (DEX) platforms facilitate the exchange of various cryptocurrencies, tokens, and assets, utilizing the principles of blockchain technology to execute trades securely and efficiently.
DEX & CEX are places where you do crypto transactions, Crypto wallets are the place where you will be storing your cryptocurrencies, like the bank where we deposit our cash.
Benefits of Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
1. Enhanced Security: DEX minimizes the risk of hacking or theft associated with centralized control of funds.
2. User Empowerment: Users maintain control over their assets, reducing reliance on third-party intermediaries.
3. Global Accessibility: DEX platforms enable trading from anywhere in the world without geographical restrictions.
4. Reduced Fees: Typically, DEX platforms charge lower fees compared to centralized counterparts, enhancing cost-efficiency for traders.
5. Resilience to Censorship: DEX platforms operate independently of regulatory constraints or censorship, ensuring uninterrupted trading.
How Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) Work
Decentralized exchanges (DEX) operate on the principles of blockchain technology and smart contracts, redefining the traditional concept of centralized exchanges. Understanding the workings of DEX involves delving into several core components:
A. Blockchain & Smart Contracts
1. Blockchain Foundation: DEX operates on a decentralized network, leveraging blockchain technology. This ensures transparency, immutability, and security by recording all transactions on a distributed ledger.
2. Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts facilitate the exchange process on DEX. They automatically execute trades when predefined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
3. Decentralization Principles: DEX embraces decentralization, meaning there’s no central authority governing the platform. Instead, it relies on a network of nodes and consensus mechanisms for validation and transaction confirmation.
B. Order Matching and Execution on DEX
1. Peer-to-Peer Trading: DEX facilitates peer-to-peer trading directly between users, allowing them to trade cryptocurrencies without the need for an intermediary.
2. Order Books and Execution: Orders are matched through various methods like Automated Market Makers (AMMs) or order book models. AMMs, like those used in platforms such as Uniswap, use liquidity pools and algorithms to determine asset prices instantly.
3. Instant Settlement: Once the terms of a trade are met, smart contracts execute the transaction automatically, transferring assets between the involved parties securely and swiftly.
C. Liquidity Provision in DEX
1. User-Provided Liquidity: DEX relies on liquidity provided by users who deposit their assets into pools. These pools facilitate the trading of different cryptocurrencies, ensuring there’s enough liquidity for transactions to occur.
2. Liquidity Pools and Rewards: Participants in liquidity pools earn rewards in the form of transaction fees or tokens for providing liquidity. These incentives encourage users to contribute to the liquidity pools, enhancing the overall liquidity of the platform.
3. Impermanent Loss: Liquidity providers face the risk of impermanent loss due to fluctuations in asset prices. It’s crucial to understand this risk and its implications while providing liquidity in DEX.
Advantages of Decentralized Exchanges
A. Security and Trustlessness
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) operate on blockchain technology, ensuring a higher level of security compared to centralized counterparts. Here’s why:
1. Elimination of Single Points of Failure: DEX doesn’t store users’ funds in a central repository, reducing the risk of hacking or server downtime, which often plagues centralized exchanges.
2. Non-Custodial Trading: Users retain control of their private keys and funds throughout the trading process, reducing the risk of theft or unauthorized access by third parties.
3. Trustless Transactions: Smart contracts execute trades automatically once conditions are met, removing the need for intermediaries and decreasing the possibility of manipulation or fraud.
4. Immutable and Transparent Transactions: Transactions on DEX are recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and immutability, which fosters trust among users.
B. User Control and Privacy
DEX empowers users with greater control over their transactions and enhances their privacy:
1. Self-Custody of Assets: Users maintain control over their assets without relying on third-party custodians, giving them complete ownership and autonomy.
2. Pseudonymity: DEX transactions often require minimal personal information, preserving user privacy by reducing the exposure of sensitive data.
3. Permissionless Access: DEX typically allows anyone to participate without requiring extensive KYC (Know Your Customer) procedures, enabling more inclusive access to financial services.
4. Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: Since DEX doesn’t aggregate user data in centralized servers, the risk of large-scale data breaches is significantly lower.
C. Lower Fees and Global Accessibility
The cost-effectiveness and accessibility of DEX make them an attractive choice for traders:
1. Reduced Trading Fees: DEX generally have lower fees compared to centralized counterparts since they eliminate intermediaries and associated overhead costs.
2. 24/7 Accessibility: DEX operate 24/7 without geographic restrictions, allowing users worldwide to participate in trading at any time, enhancing global accessibility.
3. Inclusive Nature: DEX facilitate peer-to-peer transactions, enabling users from regions with limited access to traditional banking systems to engage in global finance.
4. Empowering Financial Freedom: With lower entry barriers and fees, DEX empower users, especially those in underserved communities, to access financial services and invest in assets easily.
Challenges and Limitations of DEX
A. Liquidity Issues Compared to CEX
Decentralized Exchanges often encounter liquidity challenges compared to their centralized counterparts. This issue stems from the distributed nature of DEX, where liquidity pools may not be as deep as those in centralized exchanges. Factors contributing to this include:
1. Fragmentation of Liquidity: DEX liquidity is spread across various decentralized platforms, leading to fragmented markets and lower overall liquidity.
2. Limited Trading Pairs: Some DEX platforms may have fewer trading pairs available, reducing the attractiveness for traders looking for diverse options.
3. Impermanent Loss: Liquidity providers on DEX face the risk of impermanent loss, discouraging some from providing liquidity, thus impacting overall liquidity availability.
B. User Experience and Interface Challenges
One of the significant hurdles for DEX adoption lies in user experience and interface complexities:
1. Complexity for New Users: DEX platforms often have intricate interfaces, making them less user-friendly for newcomers to the crypto space.
2. Transaction Speed and Costs: DEX transactions might suffer from slower execution speeds and higher gas fees due to blockchain congestion, affecting user experience.
3. Custodial Risks: Non-custodial nature means users are responsible for their private keys, increasing the risk of loss if users aren’t cautious.
C. Regulatory Concerns and Compliance
1. Regulatory Uncertainty: DEX platforms operate in a regulatory gray area in many jurisdictions, leading to uncertainty and potential legal challenges.
2. KYC and AML Compliance: Lack of Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) measures in some DEX platforms might pose regulatory risks.
3. Potential for Regulatory Intervention: Governments and regulatory bodies may impose restrictions or regulatory frameworks affecting DEX operations, impacting their growth and accessibility.
Popular Decentralized Exchange Platforms
| Features | Uniswap | SushiSwap | PancakeSwap | Curve Finance | 1inch Exchange |
| Launch Year | 2018 | 2020 | 2020 | 2020 | 2019 |
| Protocol | Automated Market Maker (AMM) | AMM | AMM | Stablecoin focused AMM | Aggregator for DEXs |
| Token | UNI | SUSHI | CAKE | CRV | 1INCH |
| Mainnet | Ethereum | Ethereum | Binance Smart Chain (BSC) | Ethereum | Ethereum |
| Liquidity Pools | Wide range | Various pools | Various pools | Stablecoin-focused pools | Access to multiple DEXs |
| Governance Token | Yes (UNI) | Yes (SUSHI) | Yes (CAKE) | Yes (CRV) | No |
| Fee Structure | 0.3% | 0.3% | Varies | Varies | Aggregator fee |
| Yield Farming | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Security | Audited | Audited | Audited | Audited | Audited |
| Notable Feature(s) | Leading AMM | Community governance | BSC integration | Stablecoin-focused AMM | Aggregates multiple DEXs |
Future Trends and Innovations in DEX
A. Evolution of DEX Technology and Scalability Solutions
- Innovations in blockchain technology, such as Layer 2 solutions (like Rollups, Sidechains, and Plasma), aim to enhance transaction speeds and reduce costs while maintaining the security and decentralization aspects of DEX.
- Proof-of-stake (PoS) and sharding (dividing the network into smaller partitions, called ‘shards’), promises to enhance the performance of DEX platforms, making them more efficient and capable of handling a larger volume of transactions without compromising security.
B. Interoperability and Cross-Chain Trading
- The future of decentralized exchanges is poised to embrace interoperability, allowing different blockchains to communicate and transact seamlessly.
- Cross-chain trading protocols and technologies, such as atomic swaps and interoperability protocols (like Polkadot, Cosmos, and bridges), are gaining traction. These advancements facilitate the exchange of assets across different blockchain networks without the need for intermediaries, enabling users to access a wider range of assets and markets.
- The ability of DEX to support multi-chain ecosystems fosters increased liquidity, enhances user experience, and promotes innovation in the decentralized finance (DeFi) space.
C. Regulatory Adaptations and Market Growth
Decentralized exchanges are expected to adapt to these regulations, integrating compliance measures without compromising their core principles of decentralization and user privacy.
Key Takeaways
- Decentralized Exchange / DEX exchange/ DEX is where you can trade your cryptocurrency in peer to peer transaction without any intermediary.
- Offers more Secure & Transparent transaction. Transactions are based on Smart contracts & Execution in a blockchain.
- Liquidity might be compromised compared to centralized exchanges (CEX). Transactions may be delayed based on congestion. New comer’s user friendliness may be less compared to CEX.
DEX has the brightest future compared to CEX because of its Security & new advancements. Hope this blog might be sufficient for you to know about DEX.
There are smart ways to earn some FREE crypto coins such as Airdrops, ICOs, Bounty programs, Staking etc.
If you want learn & earn by trading Cryptocurrencies, you can learn in our profitz website – Practice more for overall success. You can do Scalping, Swing Trading, Investing in cryptocurrency.
Tell me in comments what do you think of DEX?
Happy Trading!
